Arbutin is obtained by reacting glucose with hydroquinone extracted from bilberry leaves, cranberry leaves, pear leaves, bear berries, and blueberries, which are native to mountainous regions. The molecular structure of arbutin is that of hydroquinone attached to glucose. Arbutin inhibits the activity of tyrosinase, which is involved in the process of melanin synthesis in the skin, suppresses excessive melanin accumulation, reduces pigmentation, helps to even out skin tone, and prevents spots and freckles. Arbutin is divided into α-type and β-type depending on how glucose and hydroquinone are linked.
β-Arbutin is produced by chemical synthesis. β-Arbutin has a lower structural stability than α-arbutin and is easily broken by UV rays and heat. Due to this characteristic, it is recommended to use skincare products with β-arbutin only at night, and when used during the day, it is recommended to be used together with sunscreen. It also has the disadvantage of being easily degraded by intracellular enzymes due to low intracellular stability compared to α-arbutin. It is α-arbutin that compensates for this shortcoming.
- CAS No. : 497-76-7
- EC Number: 207-850-3
- Molecular formula: C12H16O7
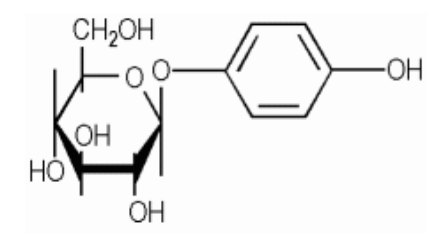
α-Arbutin can only be produced through enzymatic synthesis (microbial fermentation). Unlike β-arbutin, it is resistant to light and heat, so it can be used day and night and works stably inside the cell, making it more effective and non-toxic. By compensating for the shortcomings of β-arbutin, it is much more structurally stable and not easily broken. α-Arbutin is about 10 times more potent than β-arbutin in inhibiting melanogenesis. α-Arbutin inhibits tyrosinase to even out skin tone and minimizes aging spots, acne scars, redness after blemishes, and more. It also has antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties.
- CAS number: 84380-01-8
- EC No. : 617-561-8
- EINECS/ELINCS: 440-470-8
- Molecular formula: C12H16O7
What are the Similarities Between Arbutin and Alpha Arbutin?
- Arbutin and alpha arbutin are glycosylated hydroquinones.
- Alpha Arbutin is one of the two forms of arbutin.
- Both are derived from natural sources.
- They inhibit tyrosinase activity.
- Thus, they inhibit the formation of melanin.
- Both types reduce skin pigmentation by UV radiation from the sun.
- Moreover, arbutin and alpha arbutin act as skin-lightening agents.

What is the Difference Between Arbutin and Alpha Arbutin?
Arbutin is glycosylated hydroquinone that inhibits tyrosinase, preventing the formation of melanin, while alpha-arbutin is one of the two forms of arbutin that is more resistant to heat, shows more light stability and high water solubility properties than the other form. Thus, this is the key difference between arbutin and alpha arbutin. The safe concentration for the use of arbutin in terms of alpha form is 2 %, and beta form is 7 %.
The below infographic presents the differences between arbutin and alpha arbutin in tabular form for side-by-side comparison.
How does arbutin work on your skin?
As we know, once skin melanocytes are stimulated by external ultraviolet light, they will produce tyrosinase, which combines with tyrosine in the body to form dopamine, and finally forms melanin through REDOX, decomposition and decarboxylation reactions. Melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, is then transported to the basal layer, dermis, epidermis and other skin structure layer, and then with the dander shedding or blood circulation system discharged. However, when there is too much melanin, it can not be metabolized by the body will precipitate in the epidermal layer to form a stain. Some ingredients such as hydroquinone (hydroquinone), arbutin, phenylethylresorcinol, and azelaic acid can effectively block the binding of tyrosinase to tyrosine and inhibit melanin.
Arbutin binds effectively with the enzyme tyrosinase that catalyses the synthesis of melanin. It’s a potent alternative to hydroquinone (which is banned in Europe and Australia) but gentler on the skin. Unlike hydroquinone, which is a strong skin lightening ingredient that can be very aggressive on the skin, arbutin is a safe and natural alternative. In short, beta arbutin works by competitively inhibiting tyrosine. This prevents melanin production, making your skin appear lighter and brighter — as well as fading hyperpigmentation, age spots, sun spots and acne scars.
Post time: Jul-11-2023







