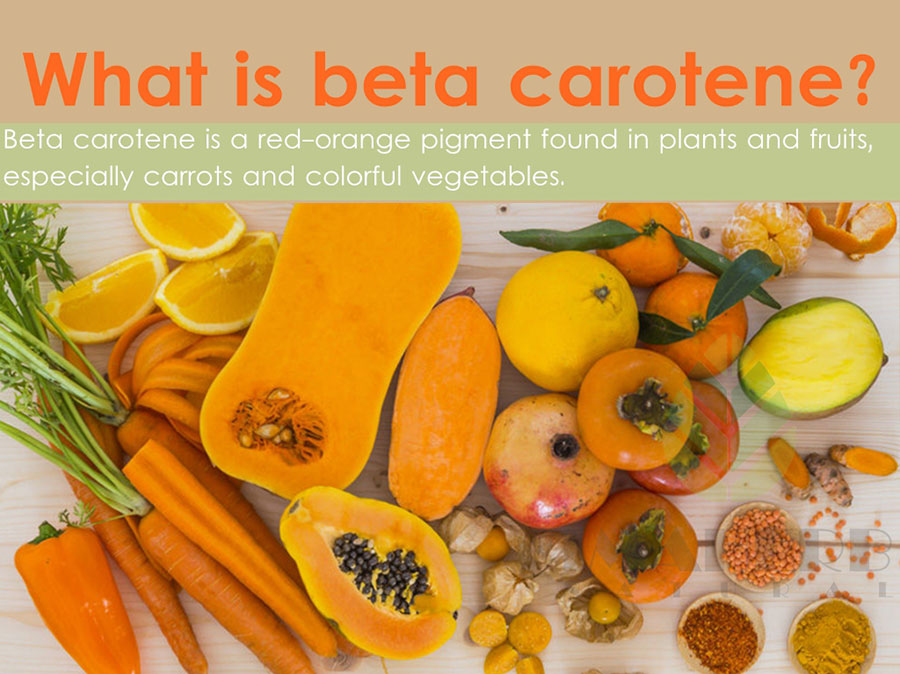
Beta carotene is a type of carotenoid, a pigment found in plants that gives them their intense color. It is orange-yellow and is found in yellow, orange, and red foods. In the body, beta-carotene is transformed into vitamin A, which is needed by the body to support healthy vision, immunity, cell division, and other functions.
This article will cover the current research and understanding of how beta carotene affects the body and which foods are good sources of this antioxidant.


Carotenoids are a group of yellow, orange, or red pigments. They can be found in fruits, vegetables, fungi, and flowers, among other living things. Beta carotene is a type of carotenoid found in vegetables such as carrots, pumpkins, sweet potatoes, spinach, and kale.
Uses & Effectiveness
Effective for
- An inherited disorder marked by sensitivity to light (erythropoietic protoporphyria or EPP)." Taking beta-carotene by mouth can reduce sensitivity to the sun in people with this condition.
Possibly Effective for
- Breast cancer. Eating more beta-carotene in the diet is linked to a lower risk of breast cancer in high risk, pre-menopausal females. In people with breast cancer, eating more beta-carotene in the diet is linked to an increased chance of survival.
- Complications after childbirth. Taking beta-carotene by mouth before, during, and after pregnancy might decrease the risk of diarrhea and fever after childbirth. It also seems to reduce the risk of pregnancy-related death.
- Sunburn. Taking beta-carotene by mouth might decrease sunburn risk in people sensitive to the sun.

Side Effects
When taken by mouth: Beta-carotene is likely safe when taken in appropriate amounts for certain medical conditions. But beta-carotene supplements are not recommended for general use.
Beta-carotene supplements are possibly unsafe when taken by mouth in high doses, especially when taken long-term. High doses of beta-carotene can turn skin yellow or orange. Taking high doses of beta-carotene supplements might also increase the chance of death from all causes, increase the risk of certain cancers, and possibly cause other serious side effects. Beta-carotene from food does not seem to have these effects.
Dosing
Beta-carotene is found in many fruits and vegetables. Eating five servings of fruits and vegetables daily provides 6-8 mg of beta-carotene. Many global health authorities recommend getting beta-carotene and other antioxidants from food instead of supplements. Regularly taking beta-carotene supplements for general use isn't recommended. Speak with a healthcare provider to find out what dose might be best for a specific condition.
Please feel free to Contact Rachel to get this goods and give you the good price.
Email: sales01@Imaherb.com
WhatsApp/ WeChat : +8618066761257
Post time: Jan-09-2023




