
Polyacrylate crosspolymer-6 is a synthetic powder ingredient that stabilizes and thickens water-based emulsions. It works particularly well to create gel textures that have a non-sticky finish and elegant slip when applied to skin. It’s also favorable for use in formulas geared toward compromised skin since it works well with other ingredients to restore skin’s barrier and prevent water loss. Chemists may also use this ingredient to help stabilise several bio-active ingredients in a single formula. Its gentleness makes it popular in eye area products as a film-forming agent. Polyacrylate crosspolymer-6 is considered safe as used in cosmetics. Typical usage ranges from 0.15–5%, depending on desired outcome.
Polyacrylate crosspolymer-6 (SEPIMAX™ ZEN) is a gelling agent and pseudo-emulsifier.
It is pre-neutralized (unlike some carbomers, which are extremely acidic and need to be mixed with a strong base like NaOH after hydrating to bring the pH up) and has a much higher electrolyte tolerance (up to 10% salt) than the similar Aristoflex AVC.

- INCI:Polyacrylate crosspolymer-6
- Appearance:Slightly lumpy white powder
- Usage rate:0.15–5%
- Texture:Polyacrylate crosspolymer-6 creates rich, velvety feeling gels.
- Scent:Nothing noticeable
- pH:3–6
- Solubility:Water
Why do we use it in formulations?
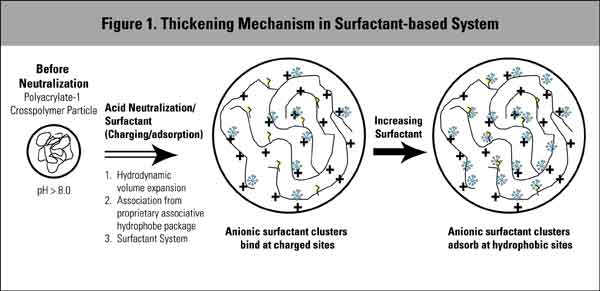
Polyacrylate crosspolymer-6 (Sepimax™ ZEN) thickens our formulations. In lower concentrations, it can suspend ingredients like glitter and exfoliants, and in higher concentrations, it can create rich feeling transparent gels and gel-creams. Polyacrylate crosspolymer-6 (Sepimax™ ZEN) can also stabilize oils, creating pseudo-emulsions, much like Aristoflex AVC.
It has a lovely sensory profile, and can be used to thicken surfactant products while also increasing and improving the foam. Polyacrylate crosspolymer-6 (Sepimax™ ZEN) works in products with pH 2–8.

Refined or unrefined?
Polyacrylate crosspolymer-6 (Sepimax™ ZEN) only exists as a refined product.
Strengths
Creates lovely, smooth gels and has a higher electrolyte tolerance than other gelling agents like Aristoflex AVC. I also like that it is pre-neutralized, meaning you don’t have to add a strong base like NaOH after hydrating it.
Weaknesses
Depending on where you live it can be difficult to find.
Alternatives & Substitutions
This will depend a lot on what you’re doing with it. If you are using Polyacrylate crosspolymer-6 as the base for a gel or gel cream I’d recommend Aristoflex AVC as an alternative, though Aristoflex AVC is very intolerant of electrolytes, so if you are counting on the electrolyte tolerance of Polyacrylate crosspolymer-6 that won’t work. You could also look at different carbomer products, like Carbopol® Ultrez 21 Polymer, though be sure to research them thoroughly to ensure they meet the needs of your product and that you are working with them properly.
If Polyacrylate crosspolymer-6 is the sole emulsifier in a formulation you will need to replace it with another gelling ingredient that will also meet the emulsifying needs of the formulation (like Aristoflex AVC—no natural single gums will work) or you will need to re-formulate to get that emulsifying power from somewhere else.
If the Polyacrylate crosspolymer-6 is serving to stabilize an emulsion at a low concentration (usually less than 0.5%) you could use Aristoflex AVC (assuming there’s no electrolyte conflict) or a natural gum like xanthan, though that will impact the end feel of the final product.
How to Work with It
Pre-disperse Polyacrylate crosspolymer-6 in the liquid oil or glycerin in a formulation before adding water or water-like ingredients (hydrosols, aloe vera juice, etc.). Cover the mixture and leave it to rest for at least an hour to allow the Polyacrylate crosspolymer-6 to hydrate, and then stir thoroughly to combine.
Pls kindly contact Alisa via sales02@imaherb.com to inquiry COA,price details
Post time: Apr-11-2024




